Belief vs. Fact — What’s the Difference? 1. What is a Belief? Definition: A personal conviction, opinion, or interpretation that someone accep
Belief vs. Fact — What’s the Difference?
1. What is a Belief?
Definition: A personal conviction, opinion, or interpretation that someone accepts as true — even if it can’t be proven.
Nature: Can be shaped by culture, religion, personal experience, or emotion.
Examples:
“I believe kindness always wins in the end.”
“I believe this policy will help families.”
Key Point: Beliefs can be deeply held and meaningful — but they are not automatically true for everyone. People have a right to believe what they want but they do not have a right to impose them on others especially in a way that restricts fairness, safety, and wellbeing. It is wrong to assert that your beliefs give you the right to enslave and/or otherwise restrict the rights of others. Plenty of wars have been fought over this very point. Throughout history the rights of women have been stripped because of male beliefs.
We Used to Believe:
1. The Earth Is Flat
For centuries, many cultures believed the Earth was a flat surface, with edges one could potentially fall off.
Ancient Greek philosophers and later scientific explorers proved the Earth is spherical. Today, “flat Earth” beliefs are fringe, not mainstream.
2. Bloodletting Cures Illness
Doctors once believed that draining blood (via leeches or cutting) balanced the body’s “humors” and cured sickness.
This practice killed more people than it healed. Modern medicine has replaced it with evidence-based practices, though leeches are used in very specific microsurgical cases today.
3. Women Are the Property of Men
Across many cultures, women were once legally considered property of their fathers or husbands. They couldn’t own land, vote, or even keep their wages.
While patriarchy is far from gone, laws worldwide have shifted slightly in a few areas—women are recognized as legal persons in their own right. Sometimes.

4. The Sun Revolves Around the Earth
For centuries, people believed the Earth was the center of the universe (the Ptolemaic model).
Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler showed that the Earth orbits the sun, which transformed science and our understanding of the cosmos.
5. Illness Is Caused by Evil Spirits
Before germ theory, people believed diseases were punishments from gods or the result of evil spirits inhabiting the body.
The discovery of bacteria, viruses, and medicine shifted this view.
✨ Pattern: Each of these beliefs gave people a sense of control or explanation, but they limited human progress until challenged. Once disproved, they opened the door to freedom, healing, and truth.
2. What is a Fact?
Definition: Information that can be proven true through observation, evidence, or measurement. Science. Even scientist-who are human beings- can be biased.
Nature: Independent of opinion, beliefs, bias, or personal feelings.
Examples:
“Water freezes at 0°C (32°F) under standard conditions.”
“The Earth orbits the sun once every 365.25 days.”
Key Point: Facts can be verified and will remain true regardless of who believes them.
DNA Carries Genetic Information
James Watson, Francis Crick, Rosalind Franklin, and others helped reveal the double-helix structure of DNA in the 1950s.
We now know DNA stores the instructions for building and maintaining all living organisms.
Women’s Pain Is Often Undervalued, But Their Threshold Can Be Higher
Studies reveal that women endure chronic pain at higher rates than men, yet their pain reports are dismissed more often in medical settings.
Research into childbirth and chronic illness suggests women have remarkable pain tolerance and resilience, developed through both biology and survival.
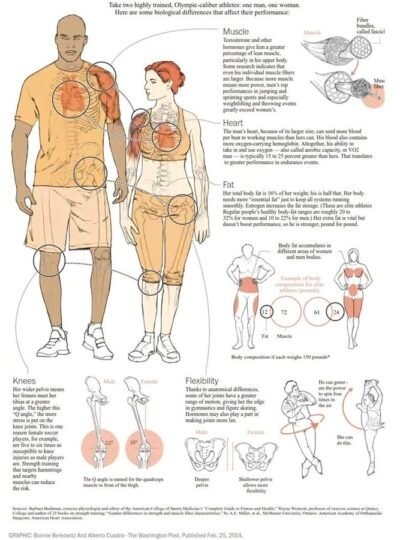
Scientific Insights on Sex Differences in Physical Performance
3. Why the Difference Matters
Facts can be tested, checked, and confirmed.
Beliefs may guide personal decisions but can’t replace verifiable evidence in public policy or safety decisions.
Beliefs vs. Facts: A Roadblock to Women’s Rights
1. When Belief is Treated as Fact
Some people present personal, religious, or cultural beliefs as if they are objective truths.
Example: “I believe women are naturally better at caregiving, so they should stay home.”
The problem: This is a belief, not a measurable fact — but it gets treated as policy guidance.
2. Facts Get Mocked and Ignored if They Challenge Beliefs
Measurable data on gender-based violence, pay gaps, or health outcomes can be dismissed because it contradicts deeply held beliefs.
Example: “I don’t believe women face discrimination anymore”
“I believe that Black women just need to be healthier in pregnancy”
“The women dying in pregnancy are poor, undereducated, who do not go to the doctor” (FALSE Educated Black women including doctors are facing the same outcome)
Despite decades of statistical evidence people will hold onto false information like a life raft with a leak in it.
3. Laws & Policies Built on Beliefs Instead of Evidence
When leaders legislate from belief, women’s autonomy and safety can be reduced.
Example: Belief-based laws on reproductive health that contradict non ideological medical consensus.
4. Shifting the Burden of Proof Onto Women
Women and girls are told to prove their reality against someone’s belief.
Example: “I don’t believe harassment happens here — show me proof” (while also ignoring existing reports. They never planned on believing the facts or evidence. They knew that when they demanded that you “prove it”.).
5. Cultural Conditioning Reinforces the Cycle
In many societies, challenging beliefs is seen as disrespect — especially if a woman challenges a man’s belief.
This makes it harder for women to insist on evidence-based decisions.
6. Weaponizing Belief to Stall Progress
“We need to respect everyone’s beliefs” is used to stop or slow policies that protect women and girls — even when those beliefs actively harm them.
✅ Bottom Line:
Facts: Can be measured, verified, and applied universally.
Beliefs: Personal and valuable, but should not outweigh evidence in decisions about women’s safety, rights, and dignity.
Belief vs. Fact in Women’s Rights
| Belief Statement | Factual Reality |
|---|---|
| “Women are naturally better caregivers, so they should stay home.” | Caregiving ability is a learned skill; both men and women can do it. Limiting women’s roles reduces economic participation and independence. |
| “Gender pay gaps don’t exist anymore.” | Global and national labor statistics show women still earn less than men for similar work, even after controlling for education and experience. |
| “Harassment only happens to certain kinds of women.” | Harassment and violence can target any woman or girl, regardless of appearance, clothing, or background. |
| “Women are safer if they don’t go out alone at night.” | Most violence against women is committed by someone they know, often in homes or familiar places — not by strangers at night. |
| “If a girl works hard enough, sexism won’t affect her.” | Structural barriers, bias, and discriminatory policies impact women’s outcomes regardless of personal effort. |
| “Men are the natural leaders in politics and religion.” | There is no biological evidence that leadership skills are tied to gender. Women lead successfully across every sector globally. |
| “Domestic violence is a private matter between couples.” | Domestic violence is a public health and human rights issue — recognized by UN and national laws as requiring societal and legal intervention. |
| “Some women lie about abuse to get attention or benefits.” | False reporting rates for abuse are very low, similar to other crimes. Underreporting is the real crisis — most survivors never come forward. |
| “Girls in our community are safe because we know everyone.” | Familiarity does not equal safety — abuse often happens within families, schools, faith spaces, and close-knit communities. |
| “Protecting women’s rights threatens men’s rights.” | Rights are not a limited resource; protecting women’s rights upholds equality and benefits entire societies. |